

Lastly the skin grafting is carried out to begin the process of re-growing skin in the burnt/affected area.
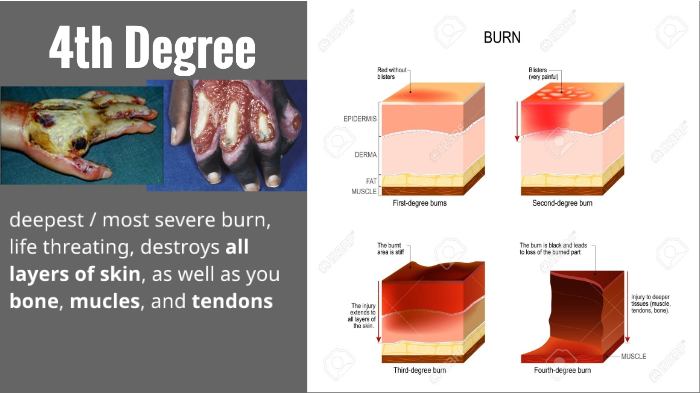
If the skin doesn’t generate new tissues, then skin grafting, may be needed. Skin Grafting: (3) As the fourth degree burns start healing, the doctor starts getting clarity on the overall extent of the damage to the victim’s body. (1) The process of removing part or all of an extremity is called amputation. It is important to remove the dead skin, as it is highly susceptible to infection and many a times it prevents the body from healing.Īmputation of the Burnt Part: (4) Amputation may be required for burns this deep. The process of removing damaged and dead skin from the burn injury is referred to as excision. (3,4) Once stabilization of patient is achieved, the process of excision begins. (2) The major organs including heart can become susceptible to inflammation in fourth degree burns.Įxcision of Burnt & Dead Skin/Tissue: The patient is often given pain medications since the treatment of the burns can be painful. Some patients may be in a state of shock, which may be due to the large inflammatory response from victim’s body. Intravenous Fluids: Intravenous fluids are given to the patient suffering from fourth degree burns to prevent low body temperature and dehydration. (3)ĭepending on the location of the burn and patient’s condition, either antibiotics can be administered orally or intravenously and topically at the site of the burn injury. The doctor may prescribe medications to alleviate the pain, apply antibiotic ointments if the doctors suspect any infection on the affected part and prescribe tetanus injection after confirming from the victim that he hasn’t had the shot in the last 10 years. Medications: The options of treatment for fourth degree burns depend upon the extent to which an individual muscles, bones and nerves are affected. Generally the loss of function in fourth degree burns leads to amputation. Excision is required often if there is damage to the muscle and this leads to loss of function of the affected part. Our body does not re-grow bone or muscle, as it re-grows the skin. Muscle Damage Causing Loss of Function & Amputation in Fourth Degree Burns: (1, 3, 4) Fourth degree burns completely destroy the skin’s upper layers of skin and start damaging the underlying muscle.Charring is also a characteristic in third degree burns sometimes, but it is more common in fourth degree burns that have had longer duration of exposure to the heat source. The charred presence in a burn is an indication that the burns will leave scars and require grafting. Charring in Fourth Degree Burns: (3) Charring is the process where hydrogen and oxygen from the skin are burnt due to high exposure to heat, leaving behind carbon.Such nerve damage in fourth degree burns also makes the level of burn more dangerous since the damage could be very serious, but you cannot asses it since you can’t feel the pain. Less Pain Due to Nerve Damage in Fourth Degree Burns: (3) The fourth degree burns are not that painful like the first and second degree burns and this is because the nerves, which send pain signals to our brain getting affected and this is why we do not feel the pain that much in fourth degree burns.Sometimes the burnt area may even be white in color with exposed muscle tissues and bones. The first noticeable symptoms of fourth-degree burn are a charred-looking appearance of the affected body part. Loss of Function & Charred/Whitish Appearance: Fourth degree burns result in loss of function of the affected body portion and charring.Fourth degree burns exhibit many similar symptoms to that of third degree burns, with a few additional features.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
